Printed circuit board (PCB) substrate materials are the base layers that make up the PCB. They are typically made of a combination of insulating materials (e.g. fiberglass or plastic) that provide mechanical support, electrical connectivity, and insulation. Common PCB substrate materials include:
- FR-4 (fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin)
- Polyimide
- Rogers (polymer-ceramic composites)
- Aluminum
The choice of substrate material depends on factors such as electrical performance, thermal resistance, and cost.
FR4
FR4 is a type of substrate material commonly used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards. It is made from a composite of fiberglass and epoxy resin, which gives it high mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties.
FR4 stands for “Flame Retardant 4.” It is a type of laminate material commonly used as a substrate in the manufacture of PCBs. The “4” in the name refers to its classification according to the NEMA grade system, which defines the electrical and thermal properties of insulating materials used in the electronics industry.
Advantages of using FR4 material in printed circuit boards include:
- Wide availability: FR4 is widely used in the PCB industry and is readily available, making it a cost-effective option.
- Good electrical insulation: FR4 has a high dielectric constant, which makes it an effective electrical insulator.
- High mechanical strength: The fiberglass reinforcement in FR4 gives it high mechanical strength, making it suitable for applications with high stress.
- Good temperature stability: FR4 has a relatively low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), which makes it stable under changing temperatures.
FR4 is widely used in a range of electronic applications, from consumer electronics to industrial control systems. It is also commonly used in the manufacture of single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer PCBs.
Rogers
Rogers PCB material is another type of rigid substrate material used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards. It is made from a combination of polymer and ceramic materials, which gives it unique electrical and thermal properties compared to other PCB substrate materials.
Advantages of using Rogers include:
- High thermal stability: Rogers material has a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), which means it maintains its dimensional stability under varying temperatures.
- Good electrical performance: Rogers material has low dielectric constant and dissipation factor, making it suitable for high-frequency applications.
- High thermal conductivity: Rogers material has high thermal conductivity, which helps to dissipate heat generated by electronic components during operation.
- Mechanical strength: The combination of polymer and ceramic materials gives Rogers material high mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
Rogers material is commonly used in high-frequency, high-performance electronic applications such as microwave and millimeter wave circuits, and is widely recognized for its consistent quality and reliability.
Metal-Core
Metal-core PCBs (MCPCBs) are a type of printed circuit board that use a metal base material, such as aluminum or copper, as the substrate instead of a traditional insulating material like fiberglass or plastic. The metal core provides improved thermal conductivity compared to conventional PCBs, making it suitable for applications that generate a lot of heat, such as power electronics or high-power LED lighting.
Advantages of using metal-core printed circuit boards include:
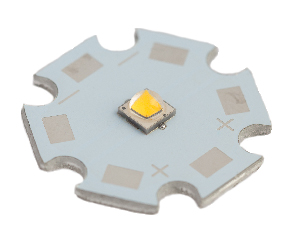
- Improved thermal management: The metal substrate provides improved heat dissipation compared to traditional PCBs, reducing the risk of thermal damage to electronic components.
- Higher operating temperatures: Metal-core PCBs can withstand higher operating temperatures, making them suitable for high-power applications.
- Increased mechanical stability: The metal substrate provides improved mechanical stability, making metal-core PCBs suitable for high-stress applications.
- Reduced weight: Metal-core PCBs are lighter than traditional PCBs, making them suitable for portable electronic devices and aerospace applications.
The choice of metal-core material depends on factors such as thermal conductivity, weight, and cost. Aluminum and copper are the most commonly used metal-core materials in MCPCBs, but other materials such as silver and nickel can also be used.
Polyimide
Polyimide PCB is a type of substrate used in flexible printed circuit boards (Flex-PCBs). It offers several benefits such as:
- High temperature resistance: Polyimide can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for use in high-temperature applications.
- Chemical resistance: Polyimide is resistant to most chemicals, including solvents and acids, making it a durable choice for harsh environments.
- Flexibility: The flexible nature of polyimide makes it an ideal choice for applications that require bending, twisting, or folding.
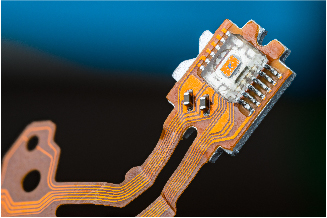
- Lightweight: Polyimide is a lightweight material, reducing the weight of the overall Flex-PCB assembly.
- Improved electrical performance: Polyimide has good electrical insulation properties, which improve the electrical performance of the Flex-PCB.
Overall, polyimide is a popular choice for Flex-PCBs due to its combination of high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, flexibility, lightweight, and improved electrical performance.
How to select the right printed circuit board material?
Each type of PCB substrate has its own advantage and is well suited for a particular purpose. When choosing the substrate for a PCB, the engineers need to take into consideration the electrical, mechanical, thermal and chemical properties of each material.
The following table compares their properties and use cases.
| PCB Material | Properties | Relative Cost | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR4 |
|
Low | General Purpose |
| Rogers |
|
High | High-Speed, Microwave |
| Metal |
|
Low | LED lighting, Motor Control, Power Circuits |
| Polyimide |
|
Mid/High | Flex and Rigid-Flex boards |
Now that you know more about the different kinds of materials used in PCB fabrication, feel free to contact PentaLogix with any request for PCB manufacturing. From regular printed circuit boards made with FR4 material to complex high frequency PCBs made with Rogers material, metalcore boards, flex and rigid flex PCBs, we are capable to help you. Reach us at (503) 828-9409 or send us an email at support@pentalogix.com